sgpgi breast cancer management
protocols
|
 |
|
|
SGPGI
Breast Cancer protocols have been prepared with the following in
mind: |
-
Views of Global experts
-
WHO/MoH guidelines
|
Department of
Endocrine & Breast Surgery
Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow,
India
Evidence-Based Pragmatic
SGPGI Breast Cancer Management Protocols (Summary)
|
|
Background: |
|
Breast cancer
management in country like ours with resource limitation and uneven
income distribution has to be approached differently from the
industrialized world. The stage at disease presentation and pathology
are different, so are the socio-economic compulsions of the patients,
necessitating emphasis on efficacious, yet safe and cheap management
strategies. A pragmatic approach to individual breast cancer patient
based on sound scientific evidence, yet keeping the socio-economic
realities and infrastructural and manpower compulsions of SGPGI have
been worked out over period of many years. Guidelines foprom various
professional bodies, meta-analysis, systematic reviews and RCT’s, along
with interpretations of contemporary data from faculty and residents of
this department as also of collaborating departments of Radiation
Oncology, Pathology, Nuclear Medicine and Radio-diagnosis have formed
the basis of these guidelines to a large extent. The first formal SGPGI
Breast cancer protocols were formulated in late 2001. Since that time,
two major revisions have been made. A summary of the third revised
version of SGPGI Breast Cancer protocols is provided here. |
|
|
|
Clinical
presentation of breast carcinoma at SGPGIMS Lucknow include |
|
|
|
Breast lump |
Usually
painless progressive
Occasional nipple discharge
Ulcerated growth
|
|
Metastatic
symptoms like weight loss, bone pain, jaundice or hemoptysis
Operated elsewhere (various degrees of surgical intervention)
Screen detected (rare)
Patients presenting for hospital based screening, out of concern for
cancer usually have- |
Breast pain
Breast nodularity
Women with family history
|
|
Patients referred
for screening/evaluation before or during HRT |
|
|
|
Approach to
breast lump/suspected breast malignancy |
|
|
|
A detailed history including |
Number of
off-springs and adequacy of breast feeding
Menopausal status, history
Onset, duration and progress of lump
Associated nipple discharge
History of trauma to breast, fever
Use of HRT, OCP
Family history of breast carcinoma, ovarian malignancy and other
related tumors in first and second degree relatives,
|
|
Diagnostic
investigation of a suspected malignancy |
|
|
|
Triple test |
Clinical
breast examination
Fine needle aspiration cytology
Mammography/USG breasts
|
|
* |
For patients
having prior intervention elsewhere, review of the histology/cytology
slides & Blocks. |
|
|
|
|
Based on the above
initial workup, a cytologically proven or suspected breast cancer is
staged clinically according to the TNM- AJCC 2002* staging system of
breast carcinoma |
|
(* Refer to 6th
edition of AJCC manual of TNM staging, also available in this course
manual in later article) |
|
|
|
Clinical stage
grouping is done for ease of communication and management planning,
as follows:- |
|
|
|
Early
breast cancer |
: |
Small
operable tumors (<5 cm), nodal status N0/N1, M0
Breast
conservation possible |
|
Large operable cancers |
: |
Large
operable tumor (>5 cm), nodal status is N0/N1, M0
Prognosis is similar to stage II disease |
|
|
|
|
Mastectomy
is possible, breast conservation is difficult |
|
Locally advanced breast carcinoma |
: |
Mostly
stage III disease: T4, N2/ N3, M0
Considered
inoperable, will require neo-adjuvant
systemic treatment |
|
Metastatic disease |
: |
Evidence
of metastasis (other than regional lymph nodal metastases)
Treated
with primary systemic treatment/palliative
measures alone |
|
|
|
|
Investigative work-up after clinical
staging: |
|
|
|
Following
minimal metastatic workup after a working diagnosis and staging is
done. In selected patients, other symptoms/signs directed test may be
employed- |
|
X ray Chest- PA
view
Blood chemistry including serum Alkaline phosphatase, LFT
Mammography if not done earlier.
If >T2 or >N1 disease, symptomatic, raised serum alkaline phosphatase-
also include |
-99mTc MDP
Skeletal Scan
-USG abdomen- to look for metastatic deposits
|
|
Clinical staging
is upgraded with any added information from imaging. |
|
|
|
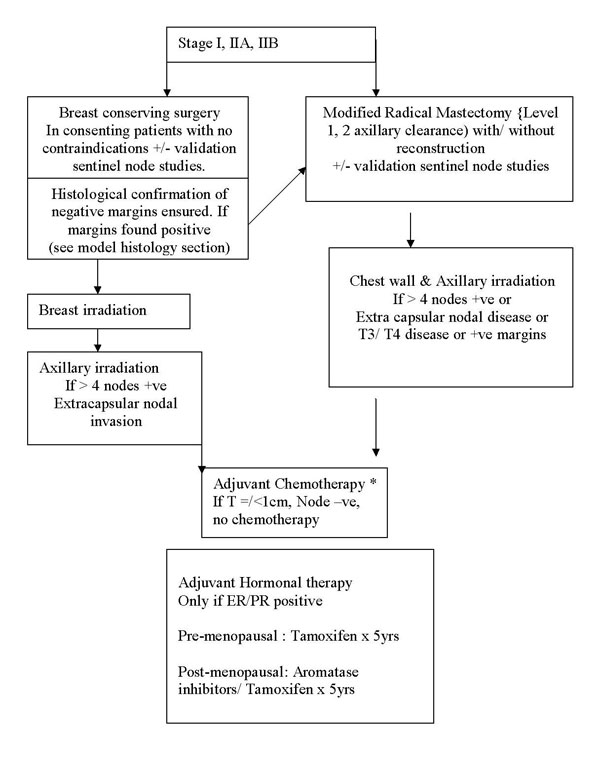
Treatment protocol for early breast cancer |
|
|
|
Early breast
cancer- T1/T2, N0/N1, M0 disease |
|
Stage I, IIA, IIB
(T2N1) |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
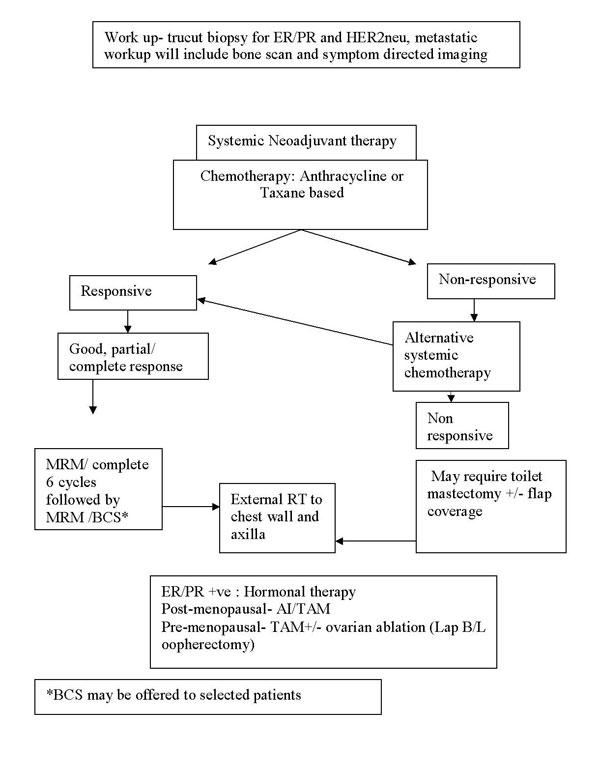
Treatment protocol for locally advanced
breast cancer |
|
|
|
Locally
advanced (and Large operable) breast cancer- Stage IIIA, IIIB, IIIC,
and IIB (T3N0M0) |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
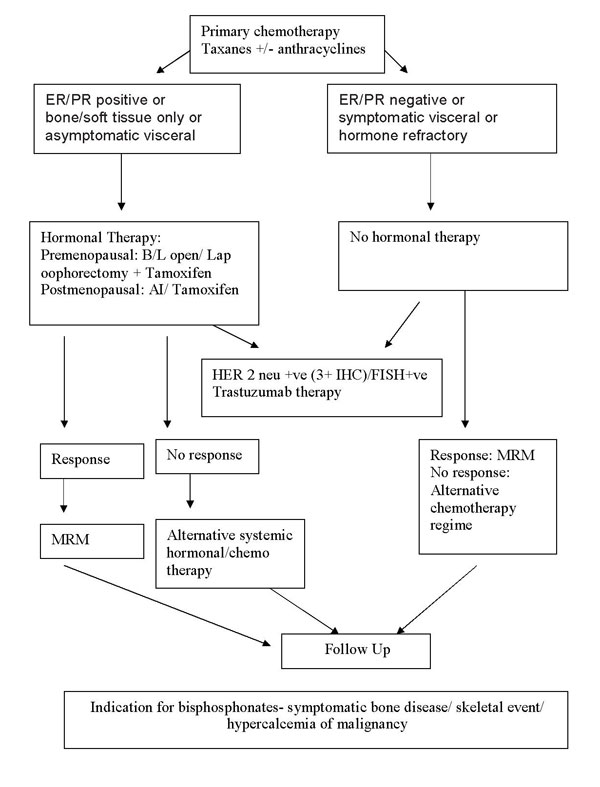
Treatment protocol for Metastatic Ca
Breast: |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Chemotherapeutic regimen and agents used commonly: |
|
|
|
Group |
Drug |
Dose |
|
Antiestrogen |
Tamoxifen |
20mg PO OD |
|
Aromatase
inhibitors |
Letrozole
Exemestane |
2.5mg PO OD |
|
HER 2
monoclonal antibody |
Trastuzumab |
4mg/kg
loading dose 2mg/Kg/week
maintenance till disease progression/1yr/critical toxicity appears |
|
|
|
|
Hormonal
agents/targeted therapy used: |
|
|
|
Regimen
|
Cycle
interval |
Drugs |
Dose |
|
CAF
|
q 21 d |
Cyclophosphamide
|
600mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
Doxorubicin
|
60mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
5 Flurouracil
|
600 mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
CEF
|
q 21 d |
Cyclophosphamide
|
500mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
Epirubicin
|
100mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
5 Flurouracil
|
500mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
AT
|
q 21 d |
Adriamycin
|
60mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
Docetaxel
|
100mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
TAC/
TEC |
q 21 d |
Docetaxel
|
100mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
Doxorubicin/
Epirubicin |
50mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
Cyclophosphamide
|
500mg/m2 IV
Day 1 |
|
|
|
|
Follow up Protocol |
|
First visit
after completing the treatment (Surgery, chemo, and radiotherapy):
starts 3 months after completion of treatment or 1 yr after initial
evaluation which ever is earlier. |
-
Clinical
breast examination
-
Hemogram
-
Blood
chemistry incl s-ALP, LFT, Ca
-
CA 15-3
(selective)
-
X ray
chest
-
ECG/ECHO
to r/o CT/RT toxicity
-
Bone
mineral densitometry
|
|
6 months post treatment: |
|
|
|
1 year after completing initial treatment: |
|
|
|
Model histology report includes: |
|
|
|
Patient name |
: |
|
Age/sex |
: |
|
Central
registration number |
: |
|
Side -
Left/Right |
: |
|
Date of
reporting |
: |
|
|
|
|
Type of specimen |
Breast
specimen- Wide local excision/Segmental excision/Mastectomy
Axillary Specimen- Axillary clearance/Axillary sampling/Sentinel
node(s) |
|
Gross Histology |
No of
lesions/Size of lesion/Site of lesion
No of nodes dissected/grossly significant nodes/Sentinel nodes
(no of blue/hot/both blue and hot) |
|
Microscopy |
Tumor
histology/grade of tumor/vascular or lymphatic invasion/margin
status of specimen No of nodes positive/extra-lymphatic
spread/sentinel node status |
|
Immunohistochemistry |
Hormonal receptor (ER/PR) and HER2neu status |
|
|
|
|
Back |
Top |
|
|